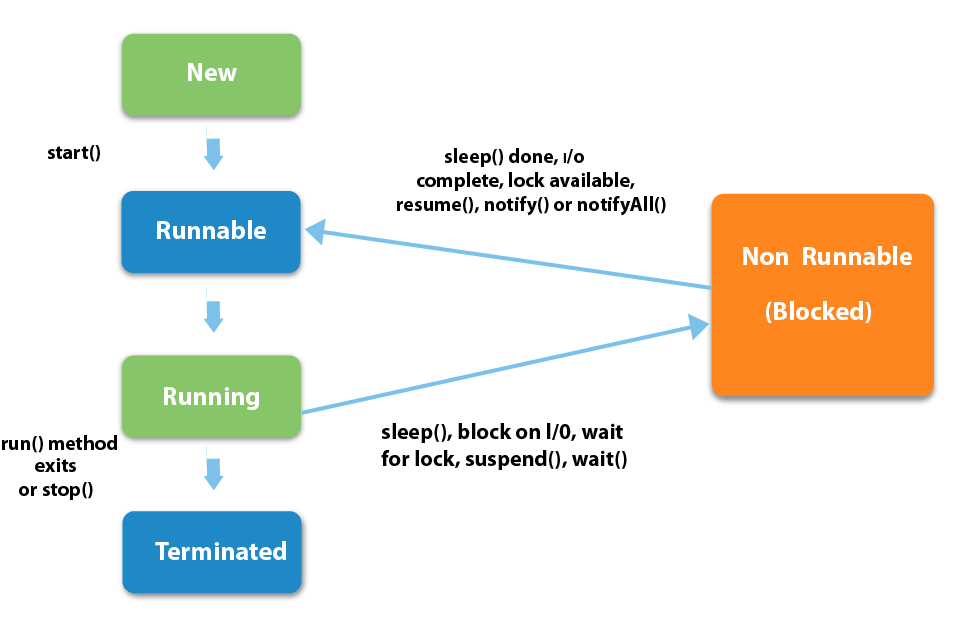
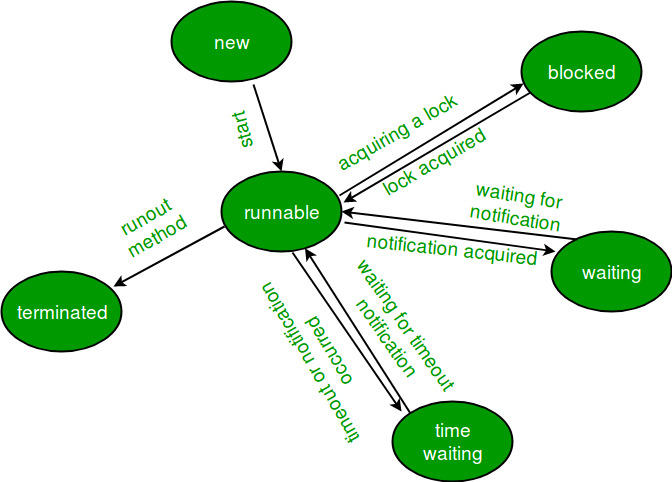
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
| public class Tester {
private static final ThreadFactory threadFactory = new ThreadFactoryBuilder().setNameFormat("pool-%d").build();
private static final ExecutorService executorService = new ThreadPoolExecutor(5, 200, 0L,
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(1024), threadFactory, new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy());
public static void main(String[] args) {
int loopTimes = 100;
testRunnable(loopTimes);
}
private static void testRunnable(int loopTimes) {
for (int i = 0; i < loopTimes; i++) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " " + i);
if (i == 30) {
CreateThreadByRunnableInterface myRunnable = new CreateThreadByRunnableInterface();
executorService.execute(myRunnable);
executorService.execute(myRunnable);
executorService.shutdown();
}
}
}
private static void testThread(int loopTimes) {
for (int i = 0; i < loopTimes; i++) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " " + i);
if (i == 30) {
Thread thread1 = new CreateThreadByThreadClass();
Thread thread2 = new CreateThreadByThreadClass();
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
}
}
}
private static void testCallable(int loopTimes) {
for (int i = 0; i < loopTimes; i++) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " " + i);
if (i == 30) {
Callable<Integer> myCallable = new CreateThreadByCallableInterface();
FutureTask<Integer> futureTask = new FutureTask<>(myCallable);
executorService.submit(futureTask);
executorService.shutdown();
}
}
}
}
|